Experiencing diarrhea can be uncomfortable and disruptive to daily life. Whether caused by a viral infection, bacterial contamination, food intolerance, or stress, diarrhea requires prompt attention to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications like dehydration. In this blog post, we’ll discuss six essential steps for providing first aid for diarrhea, empowering readers to manage symptoms effectively and promote recovery. Nitazoxanide 500 mg and Nitazoxanide 200 mg medication is used to treat diarrhea caused by certain parasite infections of the intestines.
Understanding Diarrhea:
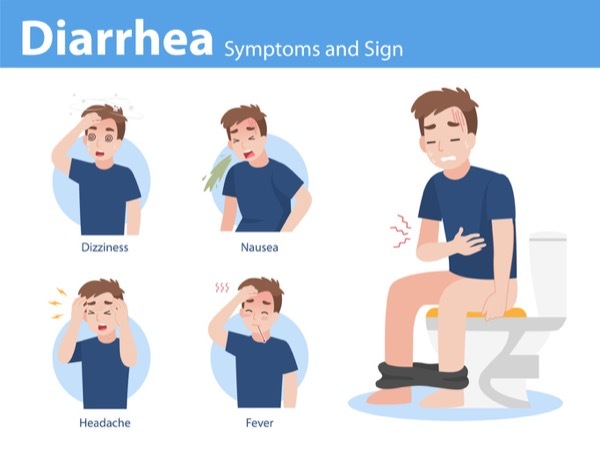
Diarrhea is characterized by loose, watery stools occurring more frequently than usual. It can be accompanied by symptoms such as abdominal cramps, nausea, bloating, and fever. Most cases of diarrhea are acute and resolve within a few days without specific treatment. However, severe or prolonged diarrhea, especially in vulnerable populations like young children or older adults, may require medical attention.
1. Hydration is Key:
The primary concern with diarrhea is dehydration due to fluid loss through frequent bowel movements. Replenishing lost fluids and electrolytes is essential to prevent complications. Encourage adequate hydration with:
- Water: Drink small amounts of water frequently throughout the day.
- Oral Rehydration Solutions (ORS): ORS solutions contain electrolytes (sodium, potassium, chloride) and glucose, helping to replace lost fluids and maintain electrolyte balance. They are particularly beneficial for children and adults with moderate to severe diarrhea.
2. Adjust Your Diet:
While eating may be challenging during diarrhea, it’s crucial to provide gentle nourishment to support recovery and prevent further irritation:
- BRAT Diet: Initially, consider bland foods like bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast (BRAT). These foods are low in fiber and can help firm up stools.
- Avoid Certain Foods: Stay away from fatty, spicy, or high-fiber foods, as they can exacerbate diarrhea. Also, limit caffeine and alcohol, which can contribute to dehydration.
3. Over-the-Counter Medications:
Several over-the-counter medications can help alleviate symptoms of diarrhea:
-
Anti-Diarrheal Medications: Medications like loperamide (Imodium) can reduce the frequency of bowel movements and improve symptoms. However, they should be used with caution and avoided in cases of fever or bloody diarrhea, as they can worsen underlying conditions.
-
Probiotics: Probiotics containing beneficial bacteria (such as Lactobacillus or Saccharomyces boulardii) may help restore intestinal balance and shorten the duration of diarrhea.
4. Practice Good Hygiene:
Diarrhea can spread easily through contaminated food, water, or contact with infected individuals. To prevent spreading or contracting diarrhea:
- Handwashing: Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water after using the bathroom and before eating or preparing food.
- Food Safety: Ensure proper cooking and storage of food to prevent contamination. Avoid consuming raw or undercooked foods, especially meats and seafood.
- Disinfection: Clean and disinfect surfaces that may have come into contact with diarrhea-causing bacteria or viruses.
5. Monitor Symptoms:
While most cases of diarrhea are self-limiting and resolve within a few days, it’s essential to monitor symptoms closely:
- Signs of Dehydration: Watch for signs such as increased thirst, dry mouth, decreased urine output, dark-colored urine, dizziness, or fatigue. Seek medical attention if signs of dehydration worsen.
- Persistent or Severe Symptoms: If diarrhea persists for more than two days, is accompanied by high fever, severe abdominal pain, bloody stools, or signs of dehydration, consult a healthcare provider promptly.
6. Seek Medical Attention if Necessary:
In some cases, diarrhea may indicate a more serious underlying condition or require medical intervention:
- Infants and Young Children: Diarrhea in infants and young children can quickly lead to dehydration. Consult a pediatrician promptly if your child has diarrhea accompanied by fever, lethargy, or signs of dehydration.
- Elderly or Immunocompromised Individuals: Individuals with weakened immune systems or chronic medical conditions may be more susceptible to complications from diarrhea. Monitor closely and seek medical advice if symptoms worsen or persist.
Conclusion:
Managing diarrhea effectively involves addressing symptoms promptly through hydration, dietary adjustments, and appropriate use of medications. By following these essential steps for first aid, individuals can alleviate discomfort, prevent dehydration, and promote recovery. Remember, while most cases of diarrhea are mild and resolve on their own, it’s crucial to seek medical attention if symptoms worsen, persist for more than a few days, or are accompanied by severe symptoms. With proper self-care and attention to hygiene, most people can manage diarrhea effectively at home and resume normal activities once symptoms improve. Always consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice and guidance based on individual health conditions and circumstances.