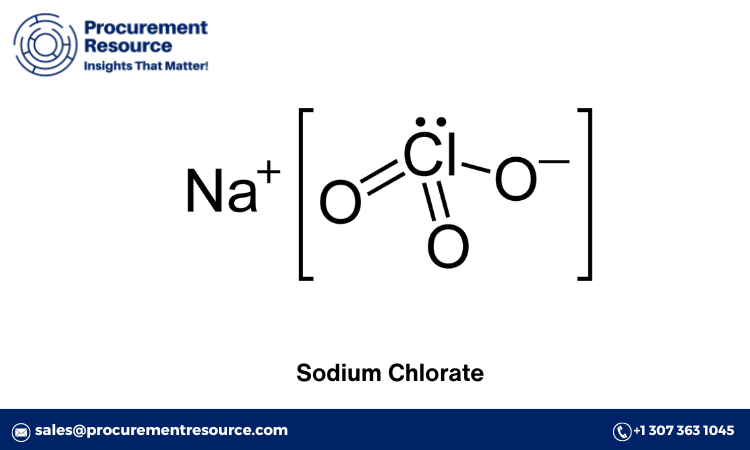
Sodium chlorate (NaClO3) is an important inorganic compound widely used in various industrial applications. It is primarily used as a bleaching agent in the paper and pulp industry, but it also finds applications in herbicides, defoliants, and the production of other chemicals. Given its significance, understanding the sodium chlorate production process and the associated costs is crucial for businesses and stakeholders in the industry. This blog will delve into the production process, the manufacturing report, raw material costs, and the latest news related to sodium chlorate production.
Sodium Chlorate Production Cost
The production cost of sodium chlorate is influenced by several factors, including raw material costs, energy consumption, labor, and overheads. The primary method of producing sodium chlorate involves the electrolysis of a sodium chloride (salt) solution. The cost structure is generally divided into fixed and variable costs. Fixed costs include expenses related to plant and machinery, while variable costs encompass raw materials, utilities, and labor.
Request For Sample: https://www.procurementresource.com/production-cost-report-store/sodium-chlorate/request-sample
Understanding these costs is crucial for manufacturers to optimize their production processes, achieve cost-efficiency, and remain competitive in the market. Let’s explore the detailed manufacturing report and process to comprehend these costs better.
Manufacturing Report and Process
Step 1: Brine Preparation
The production of sodium chlorate begins with the preparation of brine. This involves dissolving high-purity sodium chloride in water to create a concentrated salt solution. The purity of the salt and the quality of water are critical factors that impact the efficiency and yield of the subsequent electrolysis process.
Step 2: Electrolysis
The prepared brine is then subjected to electrolysis in an electrolytic cell. This cell consists of an anode and a cathode, separated by a membrane or diaphragm. When an electric current is passed through the brine solution, chloride ions (Cl-) are oxidized at the anode to form chlorine gas (Cl2), while at the cathode, water molecules are reduced to form hydrogen gas (H2) and hydroxide ions (OH-). The overall reaction leads to the formation of sodium chlorate.
Step 3: Crystallization
The electrolyzed solution, containing sodium chlorate, is then cooled and subjected to crystallization. Sodium chlorate crystals are separated from the mother liquor, washed, and dried. The mother liquor is typically recycled back into the process to improve efficiency and reduce waste.
Step 4: Purification and Packaging
The final step involves the purification of sodium chlorate crystals to ensure they meet the desired specifications. The purified product is then packaged for distribution. Quality control measures are implemented at various stages to maintain high standards.
Energy Consumption
Energy consumption is a significant component of the production cost, primarily due to the electrolysis process. The efficiency of the electrolytic cells, the voltage applied, and the duration of electrolysis all contribute to the overall energy usage. Advances in technology have aimed to reduce energy consumption, thereby lowering production costs.
Raw Material Costs
Sodium Chloride
The primary raw material in the production of sodium chlorate is sodium chloride. The cost of sodium chloride can vary depending on its source and purity. Industrial-grade salt is typically used, and its price is influenced by factors such as mining and transportation costs.
Water
High-quality water is essential for the brine preparation. The cost of water can vary depending on the location and availability of water resources. In areas where water is scarce, the cost can be a significant factor in the overall production cost.
Energy
Electricity is a major cost component due to its role in the electrolysis process. The cost of electricity varies based on local energy prices, which can be influenced by factors such as energy policies, supply and demand, and the availability of renewable energy sources.
Other Chemicals
In some cases, additional chemicals may be required for the purification and stabilization of the final product. The cost of these chemicals needs to be factored into the overall production cost.
Latest News
Technological Advancements
Recent advancements in electrolytic cell technology have focused on improving energy efficiency and reducing operational costs. Innovations such as membrane technology and high-efficiency electrodes have shown promise in lowering energy consumption during the electrolysis process. Additionally, automated control systems are being implemented to optimize process parameters and enhance overall efficiency.
Sustainability Initiatives
Environmental concerns have driven the industry towards more sustainable practices. Efforts to reduce the carbon footprint of sodium chlorate production include the adoption of renewable energy sources and the implementation of waste reduction strategies. Recycling of the mother liquor and other process by-products has become a common practice to minimize waste and improve resource utilization.
Market Trends
The demand for sodium chlorate is closely linked to the pulp and paper industry, where it is used as a bleaching agent. The growth of the pulp and paper industry, particularly in emerging markets, has positively impacted the demand for sodium chlorate. Additionally, the increasing use of sodium chlorate in herbicides and other chemical applications has contributed to market growth.
Regulatory Updates
Regulatory changes in different regions can impact the production and use of sodium chlorate. For instance, stricter environmental regulations may necessitate the adoption of cleaner production technologies, affecting production costs. Staying abreast of regulatory developments is crucial for manufacturers to ensure compliance and avoid potential disruptions.
Industry Collaborations
Collaborations between industry players, research institutions, and technology providers are fostering innovation in sodium chlorate production. Joint ventures and partnerships are enabling the sharing of knowledge and resources, leading to the development of more efficient and sustainable production processes.
Conclusion
The production of sodium chlorate involves a complex interplay of raw materials, energy consumption, and technological advancements. Understanding the production process and associated costs is essential for manufacturers to optimize their operations and remain competitive. Recent developments in technology and sustainability practices are driving the industry towards more efficient and environmentally friendly production methods. Keeping abreast of the latest news and trends is crucial for stakeholders to navigate the dynamic landscape of sodium chlorate production effectively.