Hyperprolactinemia, a condition associated with elevated levels of the prolactin hormone in the bloodstream, may have a detrimental effect on the fecundity of both both men and women. Individuals who are experiencing infertility must comprehend the effects of hyperprolactinemia on their reproductive health. This page delves into the complexities of hyperprolactinemia and its impact on fertility, as well as its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment options, and management techniques. By highlighting this frequently disregarded aspect of reproductive health, patients may have a more comprehensive understanding of the conditions they should expect when treating hyperprolactinemia and infertility.
Hyperprolactinemia were identified
When you have hyperprolactinemia, your pituitary gland produces an excessive amount of milk, even if you are not suckling your neonate. This results in an increase in the production of prolactin, the hormone that is responsible for the production of milk.
Fertility and hyperprolactinemia are linked
The delicate hormonal equilibrium that is essential for ovulation and sperm production may be disrupted by elevated prolactin levels. Before you can say “prolactin who?” your reproductive objectives may be derailed by this hormone volatility.
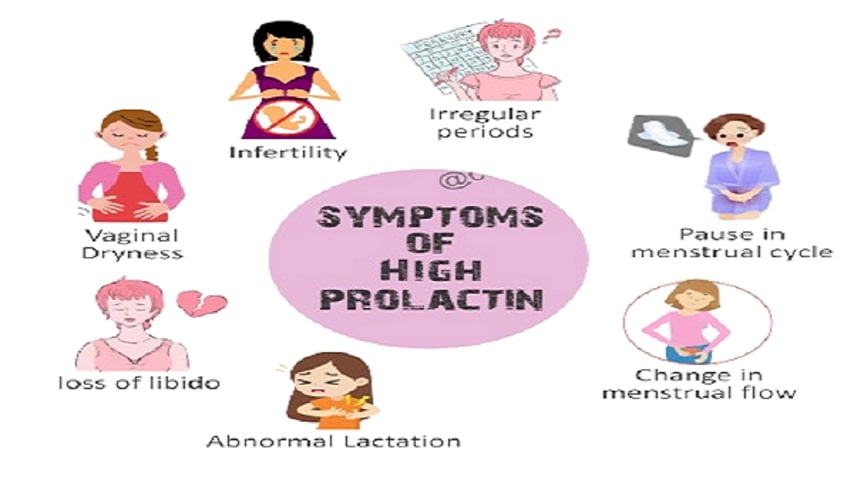
Causes and symptoms of hyperprolactinemia in both males and females
It is important to consider the production of breast milk when the time is not optimal for a child, the difficulty of conceiving, and irregular periods. Erectile dysfunction, diminished libido, and breast development may be observed in males. You have not yet submitted an RSVP for the hormonal celebration of your body.
Hyperprolactinemia in men is primarily caused by the following:
Pituitary tumors, medications, chronic renal disease, and tension are the most common causes of male hyperprolactinemia. Indeed, your body may experience hormonal overload in order to survive on a daily basis.
The fundamental causes of hyperprolactinemia in women
Pituitary tumors, certain medications, polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), hypothyroidism, or an unusual combination of hereditary characteristics may be the cause of the elevated prolactin levels in women. Not in the manner of the famous Sherlock Holmes, but rather in the manner of a hormone detective who operates within your body.
Assessments to identify hyperprolactinemia
In order to ascertain whether hyperprolactinemia is affecting your fertility, your physician may administer blood tests to assess your prolactin levels or brain imaging scans to detect any concealed tumors that may be contributing to the condition. It evokes the image of a detective program with a hormone theme, which is rife with medical drama.
The Influence of Hyperprolactinemia on Fertility Tests
Hyperprolactinemia may distort the results of your fertility testing, thereby complicating the identification of the underlying cause of your reproductive problems. It is frustrating and perplexing, akin to endeavoring to assemble a jigsaw puzzle with missing pieces.
Cabergoline 0.5mg Tablet is used to treat infertility and abnormal breast milk production (galactorrhea) caused by an excess of the natural hormone prolactin. If you’ve been sitting or lying down, stand gently to reduce the risk of dizziness or passing out.
Drugs for hyperprolactinemia
In order to facilitate the restoration of normal prolactin levels, physicians may administer medications such as dopamine agonists. Think of them as bouncers, evicting invading hormones that are causing devastation on your body.
Modes of Living and Alternative Medicine
In addition to medication, lifestyle modifications, including stress management, consistent sleep, and a nutritious diet, may assist in the regulation of prolactin levels. It is akin to hosting a low-key hormone gathering where all are invited, with the exception of the excessive prolactin.
The impact of hyperprolactinemia on irregular menstruation
Menstrual irregularities may manifest when the body’s regular hormonal equilibrium is disturbed by elevated prolactin levels. The frequency, duration, or severity of menstrual periods may fluctuate in individuals with hyperprolactinemia.
Ovulation and Hyperprolactinemia: A Correlation
Ovulation, or the discharge of eggs from the ovaries, is a critical factor in fertility. Hyperprolactinemia may disrupt the ovulation process by reducing the synthesis of hormones necessary for the process. This could potentially complicate the process of conceiving for women.
Male Reproductive Health and Hyperprolactinemia
Male and female fertility may be affected by hyperprolactinemia. Fertility may be compromised in men with elevated prolactin levels, as they may have inferior sperm quality and diminished testosterone production.
Treatment options for males with hyperprolactinemia
Prolactin-lowering medications are frequently implemented to alleviate hyperprolactinemia in men. The resolution of this hormonal imbalance has the potential to improve the reproductive health and fertility of men.
Managing Hyperprolactinemia During and After Pregnancy
Premature labor or miscarriage may result from hyperprolactinemia during pregnancy. Regular monitoring of expectant women with elevated prolactin levels by healthcare professionals is necessary to guarantee their safety.
Management of postpartum hyperprolactinemia
After giving birth, certain women may experience elevated prolactin levels, which can have an impact on their milk supply and menstrual cycle. In order to regulate hormone levels, postpartum hyperprolactinemia treatment may involve lifestyle adjustments or medication.
Cabergoline Treat high concentration of the hormone prolactin in the blood is known as hyperprolactinemia. During breastfeeding, the pituitary gland releases the hormone prolactin, which primarily boosts milk production. Among the many health issues that may arise from an abnormal rise in prolactin levels are menstrual cycle abnormalities, infertility, and erectile dysfunction. Cabergoline eliminates these issues by regulating prolactin levels.
Dietary suggestions for individuals with elevated prolactin levels
A well-balanced, nutrient-dense diet may contribute to the preservation of overall hormonal health. Although additional research is necessary in this field, certain studies suggest that cereals, barley, and verdant greens may be beneficial in reducing prolactin levels.
Alternative therapies for hyperprolactinemia
Certain patients discover that alternative therapies, including yoga, acupuncture, or stress-reduction techniques, are beneficial in conjunction with conventional therapy for managing hyperprolactinemia symptoms. When implemented in conjunction with conventional medicine, these approaches may facilitate hormonal equilibrium.
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of the illness and its treatment is necessary to regulate hyperprolactinemia and its impact on fertility. Hyperprolactinemia may be self-managed by individuals who identify the symptoms, receive an early diagnosis, evaluate treatment options, and implement essential lifestyle modifications. Those who proactively manage their hyperprolactinemia and seek ongoing medical assistance may be able to surmount the limitations of the illness and anticipate exceptional reproductive outcomes.